
Practice changing between frequencies.Make sure to ask questions about anything you are unsure of. Alternatively, your flight instructor will provide you with this information.However, if you are a new student, you can tune in to the ground control frequency and ask Ground Control for a radio check. If you're not yet a pilot, don't talk on them. Commit the emergency frequency to memory, but do not test it.ATIS, Automatic Terminal Information System.
#Cessna 172 cockpit diagram manual
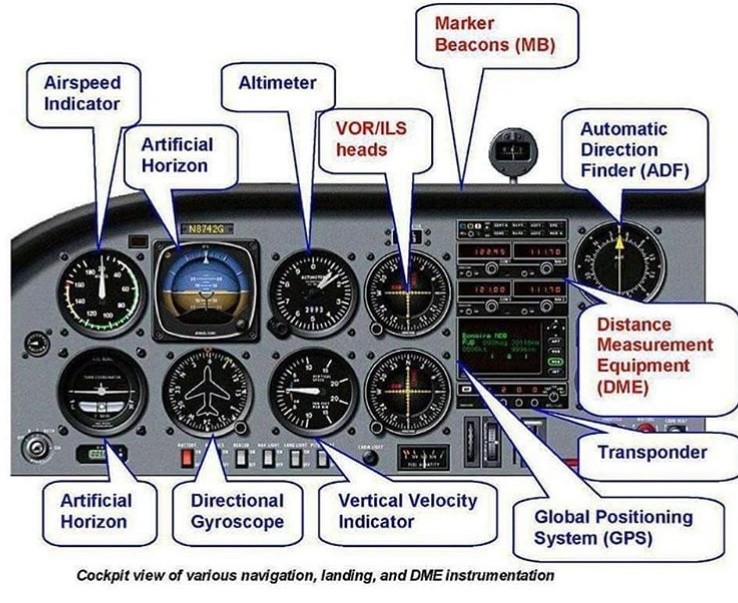
Find a radio manual and set up the radios at the required frequencies to communicate with:.
.jpg)
Find your local airport, taking particular note of your airport's required communication and navigation frequencies. Before you begin, purchase the chart at your local airport, online, or at a pilot's store, then study the chart carefully. Take care not to over-trim when landing as you may then not have enough pitch control to gain altitude quickly in case of a go-around (aborted landing). Trimming allows you to more easily maintain your direction of flight. One trims the aileron and the other trims the rudder, thereby reducing the control pressure required to operate the respective controls. Control trim – There are two trim wheels in the panel.Pressing the lower part of the pedals allows steering while on the runway. Press the top edge of the pedals and the brakes are applied. Rudder pedals – These are operated by your feet.Turn the yoke left and right to bank the aircraft. Use small pitch adjustments, in and out for pitch (to climb or descend). Yoke ("steering wheel") – This sets the attitude (climb and turn) and the speed of the aircraft.Fuel tank select – A Cessna 172 will almost always be set on "Both Tanks.".Note that the flaps should be advanced notch-by-notch one position (10°) at a time. Flaps are usually deployed to slow the aircraft to a safe speed in preparation for landing. Flaps – a flat handled switch – Used to select the wing flap positions.X Research source Note: For all practical purposes, this has to be either full-on or full-off. Carburetor heat – Used to warm the engine air intake in icing conditions, notably on long descents with the engine at low power or idling, conditions which result in a cold engine paired cold air which often cause icing.Only pull the red knob fully out when you are on the ground and ready to shut down the engine.
#Cessna 172 cockpit diagram full

(A knot is one nautical mile per hour-about 1.15 MPH or 1.85km/hr).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
